As AI moves beyond chatbots and predictive models, a new paradigm is taking shape: agentic AI, or systems designed not just to respond, but to act autonomously toward defined goals. Unlike traditional AI systems that respond passively to inputs, agentic AI can act autonomously, make decisions, and interact dynamically with its environment. For businesses and developers alike, understanding agentic AI companies, AI agent architectures, and how to create AI agents is becoming critical for staying ahead in innovation.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- What agentic AI is and why it represents a shift beyond traditional reactive systems.
- The core components of AI agent architectures and how they shape perception, reasoning, action, and learning.
- Real-world agentic AI examples, from autonomous vehicles to cybersecurity agents.
- Step-by-step guidance on how to create AI agents and integrate them into workflows.
- The role of the AI agent marketplace in lowering adoption barriers and enabling customization.
- Key benefits agentic AI delivers for businesses, including efficiency, scalability, and innovation.
- How agentic AI courses help professionals and organizations build hands-on expertise.
What is agentic AI?
Let’s start with definitions, shall we? Agentic AI refers to artificial intelligence systems designed as autonomous agents capable of taking independent actions to achieve specific goals. These AI agents are not merely reactive, but proactive. They assess situations, weigh options, and execute tasks without continuous human intervention. This capability opens new possibilities across industries, from finance and logistics to healthcare and customer service.
Core components of agentic AI
An agentic AI company specializes in designing, building, and deploying such AI agents. These companies often focus on creating frameworks, tools, and marketplaces that allow other businesses to implement agentic AI efficiently.
Understanding AI agent architecture
At the heart of agentic AI is the AI agent architecture. Understanding how AI agents are structured is key for anyone looking to create AI agents or explore agentic AI companies.
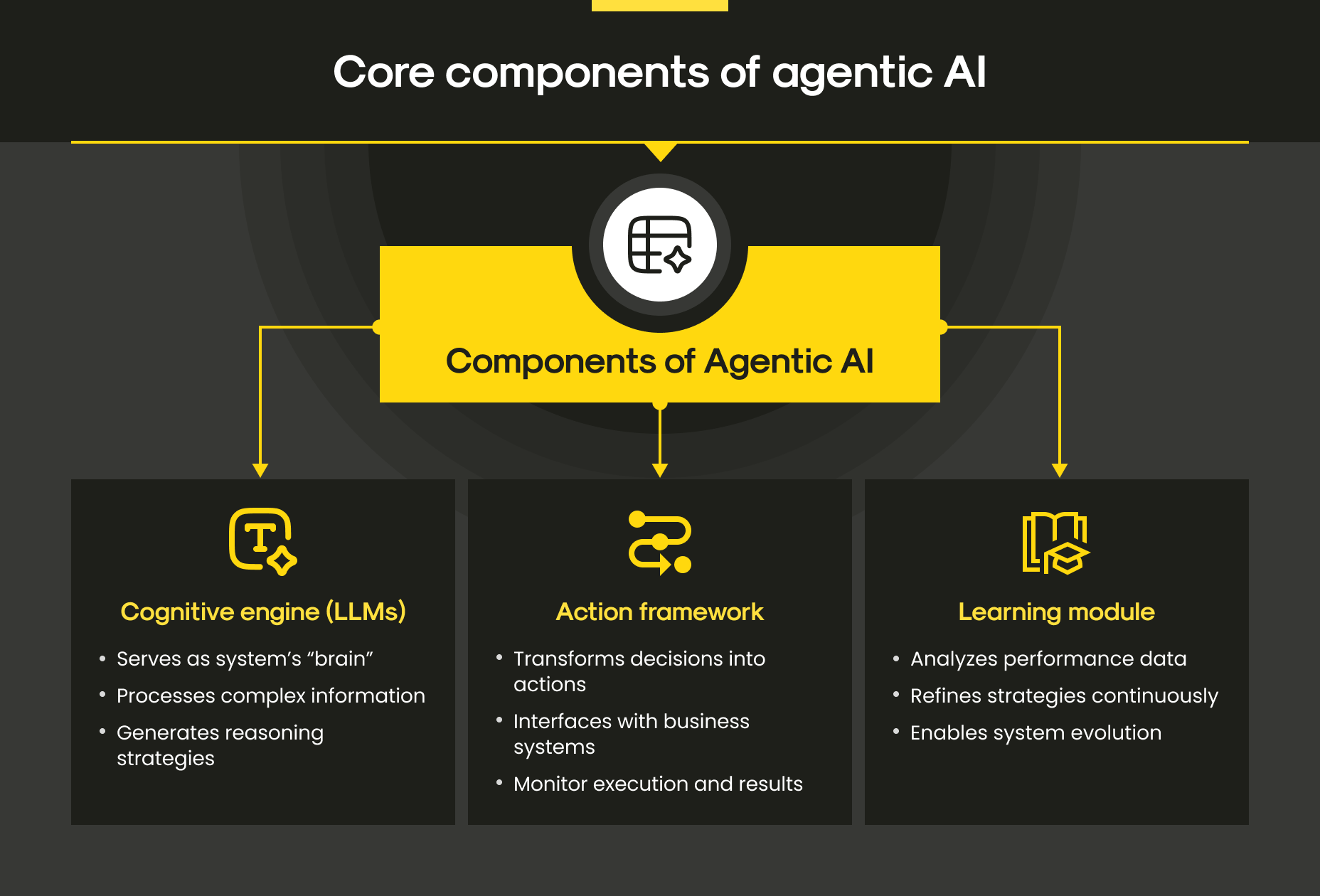
Core components of AI agent architectures
In fact, behind every effective agentic AI system lies a structured design. While implementations vary, most AI agent architectures share a set of core components that define how agents sense, think, act, and improve.
- Perception and observation
AI agents continuously gather data from their environment through sensors, APIs, or digital inputs. This information feeds into the agent’s decision-making pipeline. For example, a retail AI agent might monitor inventory levels, sales trends, and customer interactions simultaneously. - Reasoning and decision-making
Once the data is collected, the agent processes it using decision-making algorithms. This stage relies on advanced machine learning models or logic-based reasoning to determine the optimal course of action. - Action and execution
After deciding, the AI agent acts. Actions can range from sending an email, triggering a robotic arm, or initiating a financial transaction. Effective agent architecture in AI ensures that these actions align with the agent’s goals. - Learning and adaptation
Agentic AI systems learn from experience. Over time, the AI agent refines its decision-making strategies based on past outcomes, improving performance in dynamic environments.
Different AI agent architectures exist, from single-purpose reactive agents to multi-agent systems that coordinate complex tasks. AI agent architectures can also be modular, enabling integration with other systems or agents, a feature many agentic AI companies emphasize.
Examples of agentic AI
Naturally, practical examples demonstrate the transformative potential of agentic AI. Here are several agentic AI examples illustrating how these systems operate:
- Autonomous vehicles
Self-driving cars act as independent agents. They navigate traffic, respond to obstacles, and make safety decisions in real time, all without human intervention. Companies specializing in AI agent architecture for autonomous driving have created complex multi-layered architectures combining perception, reasoning, and action. - Virtual personal assistants
Beyond simple chatbots, advanced virtual assistants act proactively. They manage schedules, execute tasks, and even anticipate user needs. These AI agents are often offered via AI agent marketplaces where businesses can adopt or customize agents. - Cybersecurity agents
Security AI agents monitor networks, detect anomalies, and autonomously respond to threats. These agents leverage specialized agent architecture in AI to analyze vast datasets and act faster than human operators. - Financial advisory agents
Investment AI agents analyze market trends, recommend trades, and execute financial strategies. Their AI agent architectures integrate real-time data feeds, predictive analytics, and automated execution tools.
A notable agentic AI example is an AI agent that autonomously manages, say, a small e-commerce business. It monitors inventory, adjusts pricing, communicates with suppliers, and optimizes marketing campaigns, all with minimal human input. This illustrates the immense potential for businesses adopting agentic AI systems.
How to create AI agents
If you’re interested in joining the ranks of agentic AI companies, understanding how to create AI agents is essential. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Define the objective
Identify the problem the AI agent will solve. Clear goals guide the design of the AI agent’s architecture and functionalities. - Collect and prepare data
Data is the fuel for AI agents. Gather relevant datasets and preprocess them to ensure consistency and quality. - Select the model
Depending on your goals, choose appropriate machine learning or reinforcement learning models. Multi-agent environments may require complex architectures. - Design the AI agent architecture
Decide on the core components: perception, reasoning, action, and learning. Consider how your AI agent will interact with humans, other agents, or systems. - Train the agent
Using historical data or simulations, train the AI agent to make informed decisions. Iterative refinement ensures that the agent learns effectively. - Test and validate
Deploy the AI agent in controlled environments to evaluate performance, identify weaknesses, and ensure alignment with goals. - Deploy and monitor
After testing, integrate the agent into real-world operations. Continuous monitoring is critical for improvement and risk management.
Many online platforms provide resources to create AI agents with minimal coding. Additionally, there are agentic AI courses designed to teach the practical aspects of building and managing autonomous agents, ideal for aspiring developers and businesses.
The AI agent marketplace
Nowadays, the rise of AI agent marketplaces has made adopting agentic AI easier than ever. These marketplaces provide pre-built agents for various tasks, allowing businesses to experiment without starting from scratch. Key features include:
- Pre-trained AI agents
Agents designed for specific domains, such as customer support, logistics, or marketing. - Customizable agents
Businesses can adjust agent behaviors, integrate proprietary data, and tailor AI agents to unique workflows. - Collaborative ecosystems
Some marketplaces facilitate agent-to-agent interactions, enabling multi-agent collaboration for complex tasks.
These marketplaces lower the barrier for companies seeking to implement agentic AI solutions and highlight the growing ecosystem around agentic AI companies.
Benefits of agentic AI for businesses
In fact, adopting agentic AI can transform operations in several ways:
- Operational efficiency
Autonomous agents reduce manual effort, allowing human staff to focus on high-value tasks. - Proactive decision-making
Agentic AI agents can anticipate issues, optimize workflows, and provide real-time recommendations. - Scalable solutions
Multi-agent systems enable businesses to scale operations without proportional increases in human resources. - Innovation enablement
Companies leveraging AI agents architecture can experiment with new products and services faster, reducing time-to-market.
By partnering with an experienced agentic AI company or learning how to create AI agents internally, businesses gain a competitive edge in a digital-first world.
Training and courses in agentic AI
As agentic AI moves from theory to practice, the demand for skilled practitioners is growing rapidly. For professionals and organizations looking to deepen their expertise, agentic AI courses offer structured learning on the topic. These courses typically cover:
- Fundamentals of agent architecture in AI
- Design and implementation of autonomous AI systems
- Practical exercises in creating and deploying AI agents
- Case studies featuring agentic AI examples from industry
Completing an agentic AI course equips teams to build, deploy, and manage AI agents effectively, ensuring alignment with business objectives and technological standards.
The future of agentic AI
All in all, the potential of agentic AI is enormous, to say the least. Future trends likely include:
- More autonomous agents
AI agents capable of managing increasingly complex systems without human oversight. - Integration across platforms
Multi-agent ecosystems where agents from different providers interact seamlessly. - Ethical and transparent AI
Improved standards for responsible AI agent behavior, reducing biases and ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks. - Wider accessibility
Expanded AI agent marketplaces and accessible tools for creating AI agents will allow more businesses to harness agentic AI.
The convergence of technology, data availability, and advanced architectures will continue to accelerate adoption of agentic AI across industries, solidifying the role of agentic AI companies as innovators of the future.
How Mitrix can help
At Mitrix, we deliver AI/ML and generative AI development services that help companies:
- Design intelligent bots that understand supply chain workflows
- Integrate chatbots with tracking systems, CRMs, ERPs, and TMSs
- Build multilingual, multi-channel support agents (WhatsApp, web, SMS)
- Monitor performance and apply machine learning for ongoing improvements
We also design end-to-end fine-tuning pipelines: selecting base models (LLM comparison), preparing data, running cost-efficient LLM training (LoRA & instruction tuning), and deploying with monitoring and compliance. We also benchmark-tuned models against public leaderboards and custom domain tests so you know the real business impact.
We help companies turn AI hype into practical outcomes:
- Build AI agents tailored to your workflows
- Integrate systems seamlessly across CRM, ERP, and support platforms
- Monitor performance and continuously improve AI outputs
- Ensure compliance, ethical standards, and reliable operation
With the right approach, businesses can ship faster, avoid tech debt, and unlock new forms of value without losing sight of the human creativity that drives innovation forward. Contact us today!
Summing up
Agentic AI represents a significant leap from reactive AI systems to autonomous, goal-driven agents capable of operating independently. Understanding AI agent architectures, exploring agentic AI examples, and knowing how to create AI agents are crucial steps for any organization looking to leverage this technology. The rise of AI agent marketplaces, coupled with the expertise of leading agentic AI companies, makes it easier than ever to deploy AI agents that enhance efficiency, decision-making, and innovation.
As the field matures, agentic AI will not only transform businesses but also redefine how humans and machines collaborate, signaling a future where autonomous AI agents become integral partners in achieving both strategic and operational goals.

